Marriage equality
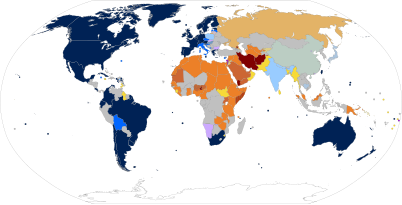
Rings indicate areas where local judges have granted marriage or imposed the death penalty in a country where that is not otherwise the law. 1May include recent laws or court decisions which have created legal recognition of same-sex relationships, but which have not entered into effect yet |
Contents
Partnership registrations
In response for the growing call for some form of recognition of same-sex relationships, the then Mayor of London, Ken Livingstone introduced the London Partnership Register in 2001. This enabled same-sex couples to have a degree of recognition by an official body of their relatiobnship, but had no legal force. It was open to opposite-sex as well as same-sex couples. Similar registers were set up in other places in the UK.The success of the London Partnership Register, and the lack of any public outcry against it, is thought to have paved the way for the introduction of civil partnerships.
Civil partnerships
Civil partnerships were introduced by the Labour Government under the Civil Partnership Act 2004. The first civil partnerships were formed in December 2005. Civil partnerships were essentially designed to parallel civil (as opposed to religious) marriage, hence the prohibion on holding a civel partnership ceremony on religious premises (this ban has since been removed) or on including any religious element in the ceremony.
One difference from civil marriage as that sex is not mentioned in the law. A marriage can be annulled if it is not consummated (ie if the couple don't have sex together) and one of the ground for divorce is adultery (ie if one of the couple has sex with someone else): there's no equivalent inthe case for either of these in the case of civil partnership. As a result the Church of England, which officially disapproves its clergy having homosexual relationships, has not banned its priests bfrom entering into civil partnerships, on the ground that they can do soand still rmain sexually celibate.